Operational efficiency is no longer achieved through scale alone. Modern businesses operate in complex, data-rich environments where speed, accuracy, and responsiveness define success. Automation and real-time monitoring have become foundational capabilities that enable organisations to manage complexity while maintaining control, reliability, and performance.
By reducing manual intervention and enabling continuous visibility into systems and processes, these technologies transform operations from reactive to proactive. Instead of responding after issues occur, organisations can identify inefficiencies, predict failures, and optimise performance in real time.
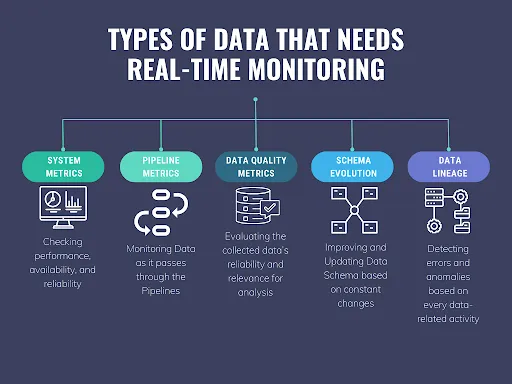
Why Businesses Are Shifting Toward Automated Operations
Businesses across industries are adopting automation to keep pace with growing operational demands and competitive pressure.
Limitations of Manual and Semi-Automated Processes
Manual processes are inherently slow, error-prone, and difficult to scale. Even semi-automated systems often rely heavily on human input for validation, exception handling, and reporting. As operations grow, these limitations lead to bottlenecks, inconsistent outcomes, and increased operational risk.
Increasing Data Volumes and System Complexity
Modern organisations generate vast amounts of data from multiple systems, applications, and devices. Managing this data manually is no longer feasible. Automation provides the structure and consistency needed to process large data volumes while maintaining accuracy and operational control.
Automation in Data-Driven Business Environments
Automation becomes most valuable when it is designed around data flows rather than isolated tasks. Industry leaders such as IBM highlight automation as a key enabler for managing complex, data-driven operations at scale.
Defining Data Automation in Modern Systems
Data automation refers to the automatic collection, processing, transformation, and routing of data across systems without human intervention. It ensures that information moves seamlessly between platforms, enabling real-time analysis and faster decision-making.
Workflow Automation and Process Standardisation
Automated workflows standardise how tasks are executed across teams and systems. This reduces variability, enforces best practices, and ensures that processes remain consistent regardless of scale or complexity.
Real-Time Monitoring: Visibility, Control, and Responsiveness
Real-time monitoring provides the operational awareness required to manage automated systems effectively.
Continuous Data Collection Across Systems
Monitoring tools continuously collect metrics, logs, and events from applications, infrastructure, devices, and networks. This continuous data stream forms the foundation for real-time visibility and performance analysis.
Live Alerts, Logs, and Performance Tracking
Real-time alerts notify teams immediately when thresholds are breached or anomalies are detected. Logs and performance metrics provide context, enabling faster root-cause analysis and corrective action.
Centralised Monitoring Dashboards
Dashboards consolidate data from multiple sources into a single, unified view. This centralisation allows operators and decision-makers to assess system health, performance trends, and operational risks at a glance.
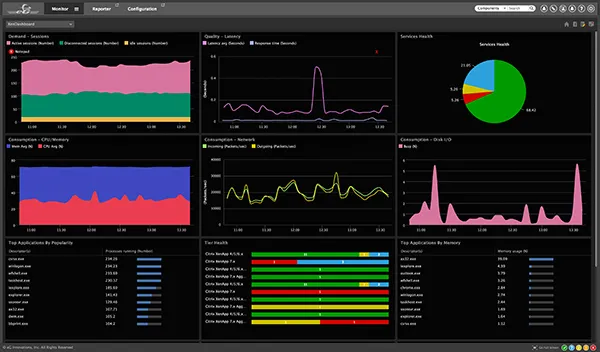
The Role of IoT in Real-Time Monitoring Architectures
The growth of connected devices has expanded the scope and value of real-time monitoring.
IoT Sensors and Edge Devices
IoT sensors collect real-world data such as temperature, pressure, energy usage, vibration, and occupancy. Edge devices process this data locally, reducing latency and enabling faster responses in time-sensitive environments.
Connectivity Protocols and Data Transmission
Reliable data transmission is achieved through protocols designed for IoT environments. These protocols balance speed, bandwidth efficiency, and reliability to ensure consistent real-time data flow.
Integrating IoT Data into Monitoring Platforms
IoT data is integrated into central monitoring platforms where it can be correlated with system and application data. This integration provides a holistic view of operations across physical and digital assets.
How Automation and Monitoring Work Together
Automation and real-time monitoring are most powerful when implemented as complementary capabilities. These capabilities form a core part of modern digital transformation strategies explored across Influencers Gone Wild.
Automated Actions Triggered by Real-Time Events
Monitoring systems can trigger automated responses when specific conditions are met. These actions may include system adjustments, workflow execution, or escalation procedures, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Reducing Human Dependency and Response Time
By automating responses to routine or predictable events, organisations minimise reliance on human operators. This significantly reduces response times and lowers the risk of errors during critical situations.
Improving Reliability and System Stability
Automated monitoring enables continuous system optimisation. Performance issues are detected early, corrective actions are applied consistently, and systems remain stable under varying workloads.
Key Benefits of Automation with Real-Time Monitoring
The combined impact of automation and monitoring delivers measurable operational advantages.
Faster and More Informed Decision-Making
Real-time data and automated analytics provide decision-makers with accurate, up-to-date insights. This enables faster responses to changing conditions and supports strategic planning based on real operational evidence.
Reduced Downtime and Operational Risk
Early detection of anomalies and automated remediation reduce system downtime. This proactive approach lowers operational risk and improves service continuity.
Optimised Resource Utilisation
Automation ensures that resources such as computing capacity, energy, and labour are used efficiently. Monitoring data highlights inefficiencies and supports continuous optimisation.
Industry Use Cases of Automated Monitoring Systems
Automated monitoring solutions are applied across a wide range of industries.
Manufacturing and Industrial Operations
In manufacturing environments, automated monitoring tracks equipment performance, production metrics, and environmental conditions. This enables predictive maintenance, reduces unplanned downtime, and improves production consistency.
IT Infrastructure and Cloud Environments
In IT and cloud operations, monitoring systems track server health, application performance, and network activity. Automation enables dynamic scaling, incident response, and workload optimisation.
Smart Buildings and Facility Management
Automated monitoring in buildings manages HVAC systems, lighting, occupancy, and security. Real-time data improves energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and operational reliability.
Energy, Utilities, and Infrastructure Monitoring
Utilities use automated monitoring to manage grids, pipelines, and infrastructure assets. Continuous data collection supports fault detection, load balancing, and long-term infrastructure planning.

Challenges and Limitations of Automation and Monitoring
Despite their benefits, these systems introduce new challenges that must be managed carefully.
Data Overload and Alert Fatigue
Excessive data and poorly configured alerts can overwhelm teams. Without proper prioritisation, critical issues may be missed among less relevant notifications.
System Integration and Compatibility Issues
Integrating automation and monitoring across heterogeneous systems can be complex. Legacy platforms may require additional interfaces or upgrades to support modern solutions.
Security, Privacy, and Compliance Risks
Automated systems process sensitive operational data. Strong security controls, access management, and compliance frameworks are essential to protect data and maintain trust.
Cost, Scalability, and ROI Considerations
Successful adoption requires careful evaluation of financial and operational factors.
Initial Implementation and Setup Costs
Automation and monitoring systems require investment in tools, integration, and configuration. Planning and phased deployment help manage complexity and reduce risk.
Scaling Automation Across Multiple Systems
As operations grow, systems must scale without loss of performance or visibility. Modular architectures and standardised interfaces support long-term scalability.
Long-Term Efficiency and Return on Investment
Over time, reduced downtime, improved efficiency, and lower operational overhead contribute to strong return on investment. Continuous measurement ensures that benefits remain aligned with business goals.
Best Practices for Implementing Automated Monitoring Solutions
Structured implementation increases the likelihood of long-term success.
Assessing Operational Requirements
Organisations should begin by identifying critical processes, performance metrics, and risk areas. Clear objectives guide tool selection and system design.
Selecting the Right Tools and Platforms
Tools should align with existing infrastructure, support integration, and offer flexibility for future expansion. Vendor ecosystems and support capabilities also matter.
Continuous Optimisation and Performance Review
Automation and monitoring are not one-time initiatives. Continuous review, tuning, and optimisation ensure that systems evolve with operational needs.
Future Trends in Automation and Real-Time Monitoring
Emerging technologies are shaping the next phase of operational efficiency.
AI-Driven and Predictive Automation
Artificial intelligence enables systems to anticipate issues, optimise workflows, and recommend actions based on predictive analysis.
Self-Healing and Autonomous Systems
Future systems will automatically detect, diagnose, and resolve issues without human intervention, further improving resilience and uptime.
Deeper Integration with Smart Infrastructure
Automation and monitoring will become embedded within smart cities, intelligent transportation, and connected infrastructure, enabling holistic operational control.
Frequently Asked Questions About Automation and Monitoring
What is the main goal of automation in operations?
To reduce manual effort, improve consistency, and enable scalable, efficient processes.
How does real-time monitoring support automation?
It provides the live data and event triggers required for automated decision-making.
Are automated monitoring systems suitable for small organisations?
Yes, scalable solutions allow organisations of all sizes to adopt automation progressively.
What risks should be considered during implementation?
Data security, system integration complexity, and alert configuration require careful planning.
Final Thoughts on Building Efficient, Automated Operations
Automation and real-time monitoring are no longer optional capabilities. Together, they form the backbone of efficient, resilient, and future-ready operations. Organisations that invest in these technologies gain the ability to adapt quickly, operate intelligently, and maintain control in increasingly complex environments. By focusing on structured implementation and continuous optimisation, businesses can achieve sustainable operational efficiency and long-term value.