Have you ever experienced those perfect days where you can spend hours outdoors soaking up the sun without any issues? Your skin feels resilient, glowing even. Yet, on other occasions, just a short time in the sunlight leads to uncomfortable redness and burning.
This variability isn’t random. There’s a fascinating connection between your body’s hormones and how sensitive your skin is to the sun’s rays.
Hormones and sun sensitivity act as the body’s chemical messengers, influencing everything from mood to metabolism. They also play a significant role in skin health and sun sensitivity, especially for women due to natural hormonal fluctuations.
Understanding this relationship can empower you to make better choices about sun exposure, skincare routines, and even the women’s vitamins you incorporate into your daily life.

A Dermatologist’s Guide to Sun Protection and Sunscreen for Summer …
What Exactly Is Sun Sensitivity?
Sun sensitivity, medically known as photosensitivity, describes an exaggerated skin reaction to sunlight exposure.
It can manifest as quick tanning, mild redness, severe sunburns, or even rashes in extreme cases.
Several factors contribute to photosensitivity, including your natural skin type (fair skin is often more prone), genetic predispositions, certain medications (like antibiotics or acne treatments), and importantly, hormonal influences.
Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun are the main culprits. There are UVA rays, which penetrate deeper and cause premature aging, and UVB rays, responsible for burning.
When these rays hit the skin, they can damage DNA in skin cells, trigger inflammation, and produce free radicals that accelerate aging and increase risks of skin cancer.
The Stages of a Sunburn | How a Sunburn Affects Your Skin
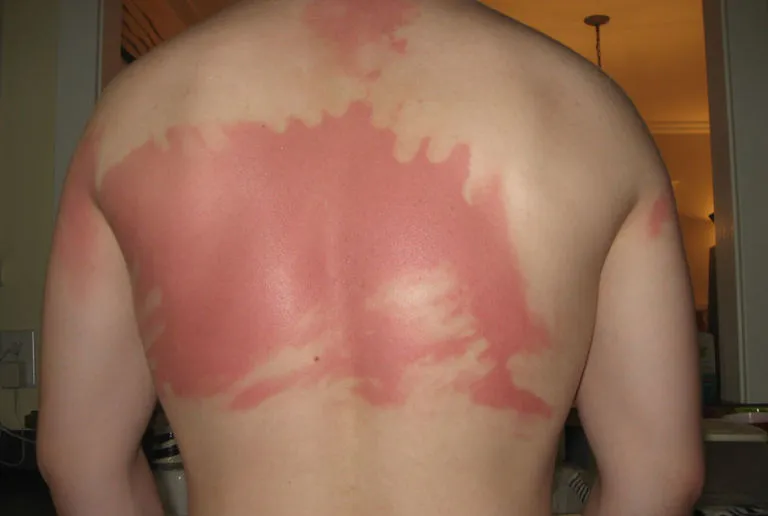
For some people, excessive exposure feels like turning into a “lobster” – red, painful, and peeling.
But why does this happen more on certain days? Hormonal shifts can alter the skin’s barrier function, hydration levels, and inflammatory responses, making it more vulnerable.
Effect of UV radiation on human skin layers | Download Scientific …
How Women’s Hormones Influence Skin Health and Sun Sensitivity
Women’s hormones fluctuate throughout life, from monthly menstrual cycles to major events like pregnancy, perimenopause, and menopause.
These changes directly impact skin thickness, moisture retention, oil production, and overall resilience to environmental stressors like UV radiation.
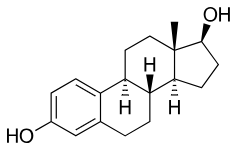
The Role of Estrogen in Skin Protection
Estrogen is the primary female sex hormone, crucial for maintaining vibrant, healthy skin.
It promotes collagen production, which keeps skin firm and elastic, enhances hydration by supporting hyaluronic acid levels, and thickens the epidermis for better barrier protection.
Higher estrogen levels often correlate with improved sun tolerance.
During the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle (days 1-14), estrogen rises steadily, peaking around ovulation.
Many women report better skin hydration, glow, and reduced sensitivity to sun during this time.
Conversely, when estrogen dips, the skin can become thinner, drier, and more prone to UV damage.
Estrogen – Wikipedia
Progesterone and Its Effects
Progesterone dominates the luteal phase (days 15-28) after ovulation.
It prepares the body for potential pregnancy but can increase sebum (oil) production, leading to acne or inflammation.
While progesterone doesn’t directly heighten sun sensitivity, its rise often coincides with falling estrogen, compounding vulnerability.
Skin may feel oilier yet more inflamed, exacerbating reactions to sun exposure.
Testosterone’s Surprising Contribution
Though typically associated with men, women produce testosterone in smaller amounts via the ovaries and adrenal glands.
It influences sebum production and can contribute to acne, especially in imbalances.
Interestingly, balanced testosterone may offer some UV protection by thickening skin in certain ways.
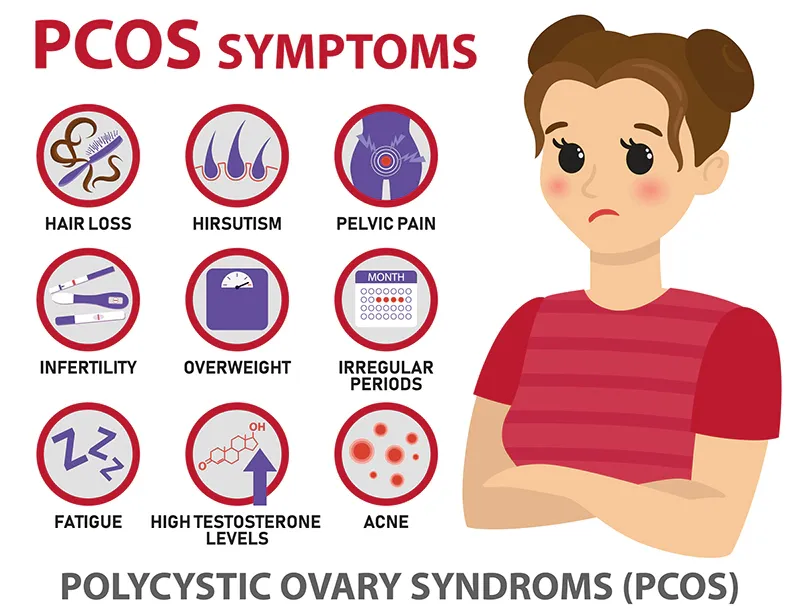
However, excess testosterone, common in conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can disrupt hormonal harmony, leading to increased photosensitivity, acne flare-ups, and uneven pigmentation after sun exposure.
Women with PCOS often experience heightened skin issues tied to sun.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Symptoms & Nutritional …
Hormonal Changes During Life Stages
Pregnancy brings surges in estrogen and progesterone, often resulting in the famous “pregnancy glow” – thicker, more hydrated skin with better sun tolerance for some.
However, others develop melasma (dark patches) due to heightened sensitivity.
Menopause marks a sharp estrogen decline, thinning skin and reducing natural protections against UV rays.
Many women notice increased sunburn risk post-menopause.

Pregnancy Glow: Definition, Causes and More
The menstrual cycle itself creates monthly variations.
Tracking your cycle can help predict days when extra caution is needed.
The Importance of Vitamin D and Balancing Sun Exposure
Vitamin D, dubbed the “sunshine vitamin,” is synthesized in the skin upon UVB exposure.
It’s essential for bone health (aiding calcium absorption), immune function, mood regulation, and even skin repair.
Safe, moderate sun exposure is the best natural source.
However, with heightened sun sensitivity due to hormones, achieving vitamin D without damage requires balance.
Many women, especially those avoiding sun or with darker skin, benefit from supplements or fortified foods.
Overdoing sun for vitamin D can accelerate aging and risks.
Aim for 10-30 minutes of midday sun a few times weekly, depending on skin type and location.
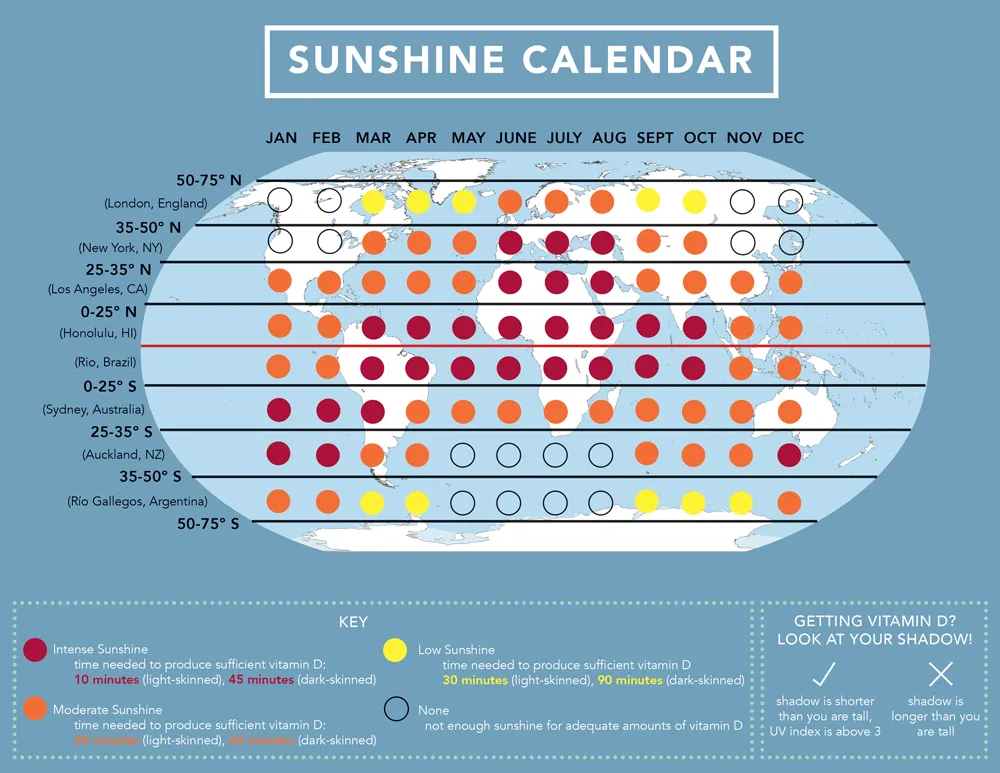
Sunshine Calendar – GrassrootsHealth
Key Vitamins for Supporting Skin Health Against Sun Damage
Beyond vitamin D, targeted women’s vitamins nourish skin internally, bolstering defenses against UV rays.
These antioxidants and nutrients promote repair, reduce inflammation, and enhance resilience.
Vitamin A: The Cell Renewal Champion
Vitamin A (retinol and beta-carotene forms) accelerates cell turnover, boosts collagen, and repairs sun-damaged skin.
It fades hyperpigmentation, smooths wrinkles, and strengthens the barrier.
Topical retinoids are popular, but dietary or supplemental vitamin A supports from within.
Sources include carrots, sweet potatoes, and liver.
Vitamin C: Brightening and Protective Antioxidant
This water-soluble vitamin neutralizes free radicals from UV exposure, preventing oxidative stress.
It stimulates collagen synthesis, evens tone, reduces dark spots, and amplifies sunscreen efficacy when taken orally.
Citrus fruits, berries, and bell peppers are rich sources.
Many women’s vitamins combine it with others for synergy.
Vitamin E: Moisturizing and Healing Powerhouse
Vitamin E, a fat-soluble antioxidant, protects cell membranes, reduces inflammation, and aids healing post-sun exposure.
It works synergistically with vitamin C, regenerating each other.
It hydrates dry skin, common during hormonal lows.
Nuts, seeds, and spinach provide natural vitamin E.
Incorporating these vitamins through diet or quality supplements can significantly mitigate sun sensitivity effects.
Consult a doctor for personalized dosing, especially if hormonal imbalances exist.
Practical Lifestyle and Skincare Tips to Manage Sun Sensitivity
Protection is multifaceted. Combine habits for optimal results.
Daily Sunscreen Use
Choose broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30+ (higher for sensitive days).
Apply generously 15 minutes before going out, reapply every 2 hours.
Mineral formulas with zinc oxide are gentler for hormone-sensitive skin.
Protective Clothing and Accessories
UPF-rated clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses provide physical barriers.
Long sleeves and pants in lightweight fabrics are ideal for hot days.

UV Protection (Sun Wear) |
Smart Timing and Shade
Avoid peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) when UVB is strongest.
Seek shade under umbrellas or trees.
Hydration from Within
Drink ample water daily. Dehydrated skin burns easier, and hormones can affect moisture retention.
Herbal teas and water-rich foods help too.
Nutrient-Rich Diet
Focus on antioxidants: berries, leafy greens, tomatoes (lycopene protects against UV).
Omega-3s from fish reduce inflammation.
A balanced diet supports hormonal health and skin repair.
Monitor Hormonal Health
Track cycles, consult for imbalances like PCOS or menopausal symptoms.
Hormone-balancing approaches (diet, exercise, stress management) indirectly improve sun tolerance.
Embracing Safe Sun Enjoyment
The interplay between hormones and sun sensitivity highlights how intricately our bodies work.
By tuning into estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone fluctuations, women can adapt routines proactively.
Combine this awareness with vitamin support, protective habits, and mindful exposure for healthier, more resilient skin.
Enjoy the sun’s benefits – warmth, vitamin D, mood boost – without the downsides.
Shine confidently, knowing you’re protecting your skin at every level.
For more
For more exclusive influencer stories, visit influencergonewild