Jurkat cells are essential in immunology research. These special cells help scientists understand how our immune system works, especially T-cells. Let’s delve deeper into what makes Jurkat cells so useful, exploring their origins, applications in fighting diseases, insights into cellular processes, and contributions to developing new medical treatments.
What Are Jurkat Cells?
Jurkat cells are like the superheroes of the lab world. They originated as regular T-cells from a boy who had leukemia. Established in the mid-1970s from the peripheral blood of a 14-year-old boy with T cell leukemia, scientists made these cells live forever in the lab through a process called immortalization. This immortalization allows for consistent experimentation without the limitations of primary cells.
These cells are special because they grow really fast, doubling in population about every 24 to 48 hours. They stay the same over time, unlike normal cells that can change unpredictably. Moreover, they act a lot like the T-cells in our bodies, making them reliable models.
Scientists can easily change their genes, which is crucial for genetic studies. Additionally, they make interleukin-2, an important molecule in the immune system that supports T-cell growth and activation.
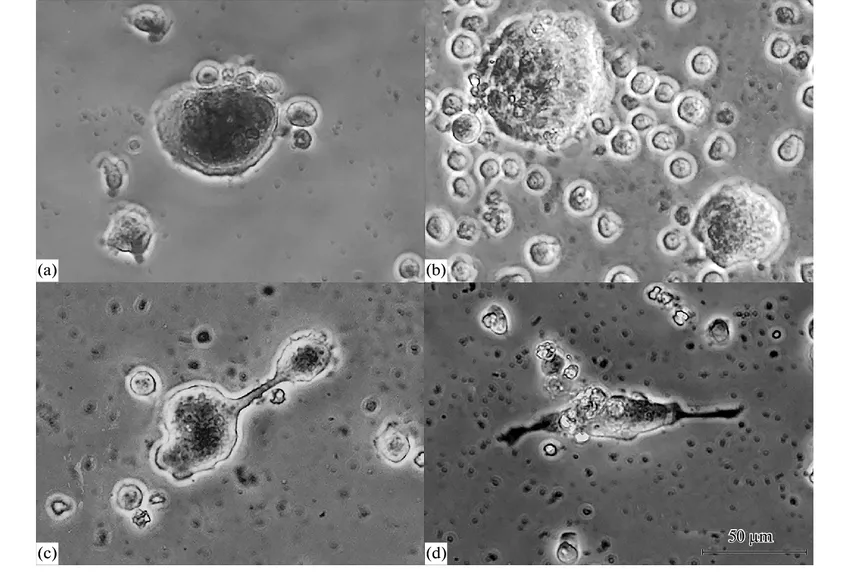
Morphology variants of large Jurkat T cells adhered to plastic …
History and Origin of Jurkat Cells
The Jurkat cell line, originally called JM, was derived from a patient with acute T-cell leukemia. Over the years, various derivatives and subclones have been developed, each with specific mutations to study particular aspects of T-cell function. For instance, clones like Jurkat E6.1 are widely used due to their stability and responsiveness.
This line has been instrumental since its establishment, providing a platform for over four decades of research. Its human origin ensures relevance to human physiology, unlike animal models.
Key Characteristics
Beyond rapid growth, Jurkat cells exhibit consistent behavior in culture. They can be stimulated with agents like phytohemagglutinin (PHA) or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) to mimic activation, producing cytokines like interleukin-2.
Their ability to express various chemokine receptors makes them susceptible to viral entry, particularly HIV, enhancing their utility in virology.
Why Jurkat Cells Are So Useful
Imagine trying to study how a car engine works while it’s zooming down the highway. That’s kind of like trying to study T-cells in our bodies. But Jurkat cells are like having a see-through engine right in the lab. Scientists can watch what happens inside these cells and learn a ton about how T-cells work, from signaling to response mechanisms.
Their ease of manipulation allows for transfection studies, where genes can be added or removed to observe effects on pathways.
Advantages in Laboratory Settings
Jurkat cells are tough and survive for a long time in culture, enabling extended experiments. They’re consistent, meaning every Jurkat cell is pretty much the same as the next one, reducing variability in results.
This consistency ensures that changes observed are due to experimental interventions, not inherent cell differences.
Flexibility in Research
They’re flexible, allowing scientists to add new genes, take away others, or change how the cells work. This helps understand what different parts of T-cells do and how to fix them when things go wrong, such as in immune disorders.
Jurkat Cells in Action: Solving Immune System Puzzles
Jurkat cells play a pivotal role in cracking the T-Cell Code. T-cells are like the brain of our immune system. They decide when to attack invaders and how to do it. With Jurkat cells, scientists can watch how T-cells make these decisions, observing which signals make T-cells wake up and start fighting, and which ones tell them to chill out.
Cracking the T-Cell Code
Studies using Jurkat cells have mapped out intricate signaling cascades. For example, upon TCR engagement, pathways involving ZAP-70, LAT, and SLP-76 are activated, leading to downstream effects like calcium flux and gene expression.
These insights have defined the T-cell receptor signaling paradigm over the past 20 years.
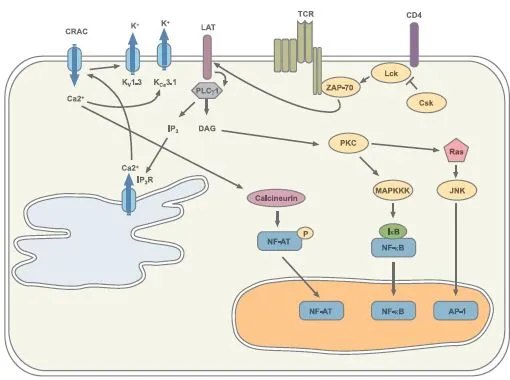
T Cell Signaling and Activation: No Simple Matter | Alomone Labs
Fighting Cancer
Cancer is tricky, and sometimes it hides from our immune system. By studying Jurkat cells, researchers are finding ways to make T-cells better at spotting and destroying cancer cells. This is helping create new treatments that boost our body’s natural defenses against cancer.
Jurkat cells are used in cancer research to study acute T-cell leukemia and other malignancies. Mutated subclones help dissect oncogenic pathways, leading to targeted therapies.
Battling Viruses
Viruses like HIV are masters of disguise. They can sneak past our immune system and make us sick. Jurkat cells help scientists understand how viruses trick T-cells and how we might be able to stop them. This research is super important for making new medicines to fight viruses.
The line’s expression of CD4 and chemokine receptors like CXCR4 makes it ideal for HIV entry and replication studies. Subclones have revealed mechanisms of viral latency and activation.

T cell and HIV interaction HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; CD4 …
T-Cell Signalling Pathways Studied with Jurkat Cells
Jurkat cells have been key in elucidating various signaling pathways. These include TCR-mediated signaling, which initiates upon antigen recognition, leading to activation of kinases like LCK and ZAP-70.
Cytokine signaling, particularly through interleukin-2 receptors, amplifies responses. Co-stimulatory pathways, such as CD28, enhance activation via PI3K-AKT.
Apoptosis signaling is studied using subclones defective in FADD or caspase-8, revealing death pathways. Other pathways, like MAPK and NF-κB, are also dissected for their roles in transcription and survival.
TCR-Mediated Signaling
This pathway involves phosphorylation cascades that activate PLC-γ1, leading to calcium release and NFAT activation. Jurkat mutants lacking PLC-γ1 have confirmed its essential role.
Cytokine Signaling
Interleukin-2 production and response are hallmarks, with JAK-STAT pathways being prominent in Jurkat studies.
Co-Stimulatory Pathways
CD28 signaling integrates with TCR to sustain activation, involving PKCθ and AP-1.
Apoptosis Signaling
Defective lines show how Fas and other receptors trigger cell death, crucial for understanding immune regulation.
Other Pathways
Additional routes like Ras-MAPK contribute to proliferation and differentiation signals.
The Superpowers of Jurkat Cells
Jurkat cells possess unique attributes that make them indispensable. They’re tough, surviving long-term culture without senescence.
They’re consistent, providing reproducible results across experiments. They’re flexible, amenable to genetic engineering like CRISPR for precise modifications.
Toughness in Culture
Unlike primary T-cells, which are hard to maintain, Jurkat cells thrive in standard media, allowing for high-throughput screening.
Consistency Across Experiments
Their clonal nature ensures homogeneity, vital for quantitative analyses.
Flexibility for Modifications
Gene editing tools enable creation of knockouts, like PTEN-deficient lines, to study PI3K regulation.
Challenges and Limitations
Even though Jurkat cells are awesome, they’re not perfect. Here are a few things scientists have to be careful about: They’re cancer cells, so they don’t act exactly like normal T-cells all the time.
They might not show everything that happens in a real immune system. Some experiments that work with Jurkat cells might not work the same way in our bodies.
Long-term culture can lead to genetic drift, altering phenotypes. Jurkat cells may not accurately represent all T-cell subsets, such as Th1 or Th2.
Genetic Abnormalities
Jurkat cells lack PTEN and INPP5D, leading to hyperactive PI3K signaling. They produce xenotropic murine leukemia virus (XMRV), potentially confounding results.
Representation Issues
As transformed cells, they exhibit unlimited proliferation, differing from quiescent primary T-cells.
Translational Limitations
Findings may not directly translate to in vivo scenarios due to the absence of full immune context.
The Future of Jurkat Cell Research
Looking ahead, Jurkat cells will continue driving advances. In personalized medicine, insights from these cells enable treatments tailored to each person’s unique immune system.
New cancer therapies, like CAR-T cells, are tested using Jurkat reporters for functionality. Better understanding of autoimmune diseases, where the immune system attacks our own body, is facilitated by pathway dissections.
Personalized Medicine
By modeling patient-specific mutations, Jurkat derivatives can predict therapeutic responses.
New Cancer Therapies
Immunotherapies, including checkpoint inhibitors, benefit from Jurkat studies on co-stimulation.
What is cancer immunotherapy? | University of Chicago News
Better Understanding of Autoimmune Diseases
Pathways like NF-κB, dysregulated in autoimmunity, are probed to develop interventions.
Conclusion: The Lasting Impact of Jurkat Cells
Jurkat cells might be tiny, but their impact on science and medicine is huge. From helping us understand how our immune system works to paving the way for new treatments for cancer and other diseases, these little cells are true heroes of the scientific world.
As research continues, Jurkat cells will keep playing a crucial role in unlocking the secrets of our immune system. Who knows what amazing discoveries they’ll help us make next? One thing’s for sure – these remarkable cells will be at the forefront of medical breakthroughs for years to come.
For more
For more exclusive influencer stories, visit influencergonewild





