Telemedicine has revolutionized the healthcare landscape, offering unprecedented access to medical services, particularly in the realm of chronic disease management. As we head into 2026, the integration of telemedicine in managing chronic conditions is expected to deepen, with new trends shaping the future of patient care. This article explores the key trends in telemedicine for chronic disease management and what to expect in the coming year. With advancements driven by technology and data, telemedicine is not just a convenience but a necessity for handling chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease). These conditions require continuous monitoring and long-term management, and telemedicine provides a bridge to more efficient, personalized care.
The growth of telemedicine is backed by impressive market projections. According to recent data, the telehealth market is expected to reach $175 billion by 2026, signaling a digital transformation in healthcare. This expansion is fueled by the need for better access in rural areas, reduced healthcare costs, and improved patient outcomes. In 2026, we anticipate even more proactive approaches, including culturally matched therapists and real-time interventions, making telemedicine a cornerstone for chronic disease management.
The Role of Telemedicine in Chronic Disease Management
Chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and COPD, require continuous monitoring and long-term management. Traditionally, this involved frequent visits to healthcare facilities, often resulting in a heavy burden on patients and healthcare systems alike. Telemedicine, however, has changed the game by enabling patients to receive timely consultations, follow-ups, and monitoring from the comfort of their homes.

With remote healthcare technologies, such as video calls, wearable devices, and mobile health applications, patients and healthcare providers can engage more frequently, allowing for real-time monitoring and more personalized care. This shift is crucial in the context of chronic diseases, where regular check-ins are necessary to prevent complications. Studies show that telemedicine interventions can reduce chronic disease risk factors, with the Community Preventive Services Task Force recommending telehealth for managing conditions like cardiovascular diseases.
For instance, in diabetes management, telemedicine allows for ongoing glucose tracking via connected devices, helping patients avoid spikes that lead to hospitalizations. Similarly, for hypertension, remote blood pressure monitoring ensures adjustments to medications without in-person visits. Statistics indicate that patients with multiple chronic conditions use telemedicine at a rate of 50%, compared to 33% for those without, highlighting its targeted impact.
The effectiveness of telemedicine is evident in reduced hospital readmissions and improved adherence to treatment plans. A systematic review found that telemedicine is associated with a 45% reduction in hospitalizations for chronic conditions. This not only lightens the load on healthcare systems but also empowers patients to take an active role in their health.
Moreover, telemedicine addresses barriers like geographic limitations. Patients in rural areas, who often face long travel times, benefit immensely from virtual consultations. This accessibility leads to earlier interventions, preventing disease progression. In heart disease management, for example, remote ECG monitoring can detect irregularities promptly, averting emergencies.
Personalized care is another hallmark. Through data from wearable devices, providers can tailor treatment plans based on individual patterns. Mobile health applications track symptoms, medications, and lifestyle factors, providing a comprehensive view. This integration fosters better patient-provider relationships, with more frequent engagements leading to trust and compliance.
Challenges exist, such as digital literacy and access to technology, but initiatives in 2026 aim to bridge these gaps through user-friendly platforms and subsidies for devices. Overall, telemedicine’s role in chronic disease management is transformative, making healthcare more proactive and patient-centered.
As we look ahead, the evolution of telemedicine will incorporate more advanced tools, ensuring that chronic conditions are managed with precision and efficiency. This foundation sets the stage for emerging trends that will further enhance outcomes.
Key Telemedicine Trends to Watch in 2026
As telemedicine continues to evolve, several trends are emerging that promise to further enhance the management of chronic diseases. Here’s what we can expect in 2026, building on current advancements and projections from industry experts.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
One of the most significant trends in telemedicine for chronic disease management is the integration of AI and ML. These technologies are expected to play a crucial role in improving diagnosis, predicting disease progression, and personalizing treatment plans.

AI in Remote Monitoring: AI-powered devices can analyze patient data in real time, identifying patterns that indicate potential complications. This allows healthcare providers to intervene earlier, improving patient outcomes. For example, AI algorithms in wearable devices can detect anomalies in heart rhythms for COPD patients, alerting doctors instantly.
Predictive Analytics: Machine learning algorithms can predict disease exacerbations based on a patient’s historical data, enabling proactive management rather than reactive treatment. Studies show that AI can forecast complications in diabetes with high accuracy, reducing emergency visits by up to 30%.
Virtual Assistants: AI-powered virtual assistants can help patients manage their daily medications, schedule appointments, and track symptoms, ensuring better adherence to treatment plans. These assistants use natural language processing to interact conversationally, making them accessible for all ages.
In 2026, AI adoption in telemedicine is projected to surge, with nearly 90% of hospitals integrating AI-driven diagnostics. This includes precision management for chronic diseases, where AI combines with wearables to predict deterioration trends. Applications span from medication adherence to lifestyle recommendations, with scoping reviews highlighting AI’s role in self-management for conditions like hypertension.
Challenges include data bias and ethical concerns, but advancements in trustworthy AI are addressing these. Overall, AI and ML will make telemedicine more intelligent, offering tailored interventions that save lives and resources.
Expansion of Remote Monitoring Devices
The use of wearable and remote monitoring devices is expected to grow significantly in 2026. These devices allow for continuous tracking of vital signs such as blood pressure, blood glucose levels, heart rate, and oxygen saturation. This data is transmitted in real time to healthcare providers, allowing for immediate interventions when necessary.

Smart Wearables: Devices like smartwatches and glucose monitors are becoming more advanced, offering more accurate data and integrating seamlessly with telemedicine platforms. By 2026, multi-sensor devices will measure ECG, SpO2, temperature, and more, bundled into compact forms.
Home Diagnostic Kits: New technologies are being developed to allow patients to conduct basic diagnostic tests at home, such as checking cholesterol levels or kidney function, and transmit the results directly to their doctors. This empowers patients with chronic conditions to monitor without frequent clinic visits.
Wireless Monitoring: Devices that measure a patient’s vitals without the need for physical contact are on the rise, offering more convenience and reducing the risk of infections in vulnerable patients. Advancements include AI-boosted remote patient monitoring (RPM) software, poised to be a major innovation.
The smart medical devices market is forecasted to reach $49 billion by 2034, starting from $28.56 billion in 2026. This growth supports chronic disease management by enabling home-based care, like remote labor monitoring or cardiac health tracking. Studies confirm RPM reduces early hospital admissions and improves outcomes.
Integration with 5G and sensors enhances data speed and accuracy, making these devices indispensable. For heart disease, wearables provide real-time alerts, while for diabetes, continuous glucose monitors adjust insulin dynamically. This trend democratizes healthcare, especially in underserved areas.
Growth of Virtual Care Platforms
In 2026, we can expect the expansion and refinement of virtual care platforms. These platforms are designed to offer a wide range of healthcare services, from consultations to chronic disease management, through digital means.
Interoperability: Virtual care platforms are expected to improve their interoperability with electronic health records (EHR) and other healthcare systems. This will allow for better data sharing and coordination of care, especially for patients seeing multiple specialists for their chronic conditions. EHR integration ensures seamless data exchange, enhancing patient satisfaction and reducing costs.
Patient Portals: More advanced patient portals will give individuals access to their medical records, test results, and treatment plans. These portals will be equipped with AI-driven features that suggest lifestyle changes or recommend specialist consultations based on the patient’s health data.
Telehealth Networks: With an increasing number of healthcare providers offering telemedicine services, we may see the rise of more comprehensive telehealth networks that provide round-the-clock care, particularly for managing chronic diseases. Platforms like these support scheduling, documentation, and billing, all while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
Interoperability remains key, with studies showing it unlocks telehealth’s potential by facilitating data across institutions. For rural healthcare, this means better e-visits and virtual consultations, lowering costs. In 2026, expect more EHR-centric tools driven through patient portals, improving care coordination.
Challenges like diverse EHR vendors are being tackled through standardized APIs, ensuring smooth integration. This trend will make virtual care more holistic, integrating primary and specialty services for chronic patients.
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy Measures
With the increasing use of telemedicine and digital health solutions, data security and privacy concerns are at the forefront. Managing chronic diseases often involves sensitive health information, making it essential that telemedicine platforms are equipped with robust security measures.

Stricter Regulations: Governments and healthcare organizations are likely to introduce stricter regulations surrounding patient data protection, including the use of encryption and secure cloud storage systems. By 2026, compliance with updated HIPAA guidelines will be mandatory for telemedicine.
Blockchain in Healthcare: Blockchain technology is gaining traction as a secure method for storing and transmitting medical data. It offers decentralized and tamper-proof data management, which could enhance trust in telemedicine solutions.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): More healthcare platforms will likely adopt multi-factor authentication to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive health information. This, combined with AI for threat detection, will bolster security.
In 2026, cybersecurity will be a dominant force, with only 56% of providers confident in current privacy measures. Emerging trends include advanced encryption and regulatory changes, like extended Medicare flexibilities. Telehealth security safeguards patient data, improving privacy through secure environments.
Challenges involve infrastructure costs and lack of physical exams, but solutions like blockchain address them. Statistics show rising cyber threats, making strategic guides essential for CIOs. Enhanced measures will build trust, encouraging wider adoption for chronic management.
Greater Focus on Mental Health Integration
Chronic diseases can take a toll not only on the body but also on mental well-being. Telemedicine is poised to play a larger role in integrating mental health services into chronic disease management. Virtual therapy sessions and remote mental health consultations can support patients who are dealing with the emotional and psychological challenges of living with a chronic illness.

Behavioral Health Integration: Telemedicine platforms will increasingly include services such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and counseling for patients with chronic conditions. This integration improves physical and mental quality of life across diseases.
Digital Therapeutics: There will be more use of digital therapeutics—evidence-based treatments delivered via digital platforms—to address both physical and mental health issues in chronic disease management.
Stress Management Tools: Many telemedicine platforms will offer tools to help patients manage stress, anxiety, and depression, all of which can impact the management of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
Telehealth supports behavioral health integration, with reports from AMA advancing sustainable models. For chronic conditions, it enhances outcomes in areas like OUD and general mental health. Over 450 million people worldwide face mental disorders, and telemedicine interventions show empirical evidence of effectiveness.
In 2026, expect accelerated integration, facilitating patient-centered care. This includes telehealth for serious mental illness and substance use, positively affecting quality of life.
The Impact of Telemedicine on Healthcare Costs
One of the biggest benefits of telemedicine is its potential to reduce healthcare costs, especially for patients managing chronic diseases. Telemedicine can cut down on unnecessary hospital visits, lower travel expenses, and reduce the need for expensive emergency interventions by catching potential issues early. In 2026, we are likely to see further adoption of telemedicine as a cost-saving tool for healthcare systems worldwide.
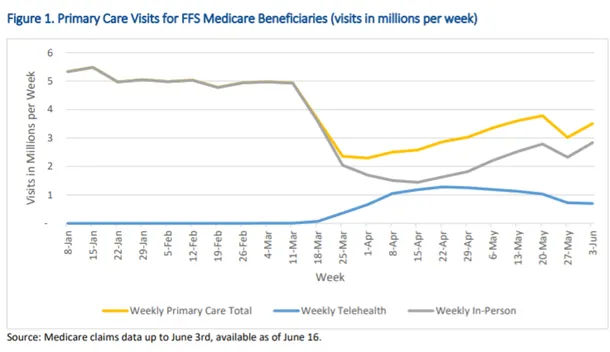
Factors Reducing Costs:
- Reduced Hospital Readmissions: Telemedicine allows for continuous patient monitoring, leading to early detection of complications, which in turn can prevent hospital readmissions. Studies estimate savings of $1814 per person during stay-at-home periods.
- Lowered Travel Costs: Patients in rural or remote areas can avoid long trips to specialist appointments by accessing care remotely. CMS projects $60 million in travel savings for Medicare patients.
- Fewer Emergency Room Visits: With regular monitoring and timely interventions, telemedicine can help avoid emergencies that arise from unmanaged chronic conditions. Virtual care could substitute $250 billion in U.S. spending.
Statistics show telemedicine lowers total medical costs, with one study linking it to reduced spending post-exposure. During COVID, it decreased costs by 8.7% per percentage point increase in usage. For cancer patients, savings average $147-$186 per visit.
In chronic management, telehealth improves adherence and outcomes, leading to lower recidivism. Policy changes in 2026 will support this, making it a sustainable cost-saver.
Conclusion
Telemedicine is set to become even more integrated into chronic disease management in 2026. Advances in AI, wearable devices, and virtual care platforms are making remote healthcare more efficient and personalized. While challenges such as data security remain, innovations like blockchain are addressing these issues. As these trends unfold, telemedicine will continue to improve the lives of millions of people living with chronic conditions, offering them more accessible, convenient, and cost-effective care.
The future holds promise with AI takeovers, interoperability implementations, and enhanced RPM. This evolution will redefine care delivery, emphasizing proactive, patient-centered approaches.
For more
For more exclusive influencer stories, visit influencergonewild