In today’s digital-first economy, businesses are under pressure to deliver fast, seamless, and engaging digital experiences. One of the most common strategic questions companies face is whether to build a mobile app vs web app. While both solutions serve digital users, their technical structure, cost, scalability, and business impact are very different.
Choosing the wrong option can lead to wasted budget, low adoption, and long-term maintenance issues. Understanding the strengths and limitations of mobile apps and web apps is essential to selecting the solution that aligns with your business goals, audience, and growth strategy.
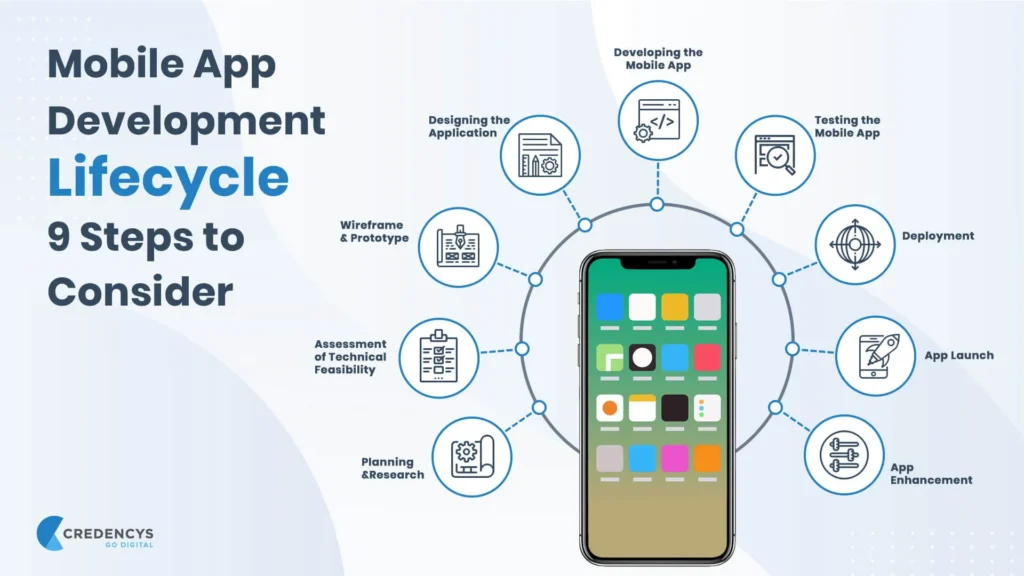
Understanding Mobile Apps and Web Apps in Today’s Digital Landscape
Digital applications have evolved rapidly as user behaviour shifted toward smartphones, tablets, and cloud-based platforms. Businesses must understand how each app type fits into modern usage patterns.
What Is a Mobile Application?
A mobile application is a software program designed specifically for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. These apps are installed directly from app stores and can access native device features like camera, GPS, biometrics, and push notifications. Mobile apps are typically optimised for performance, offline usage, and deep user engagement.
What Is a Web Application?
A web application is accessed through a web browser and does not require installation on a device. Web apps run on remote servers and are designed to work across different devices and operating systems. They are easier to update and distribute, making them ideal for content-heavy or frequently changing platforms.
How App Usage Has Evolved Across Devices
Users now switch seamlessly between mobile, desktop, and tablet devices. While mobile usage dominates in terms of time spent, web apps remain critical for discovery, accessibility, and cross-device consistency. This shift has influenced how businesses design and deploy applications.
Core Technical Differences Between Mobile Apps and Web Apps
Although mobile apps and web apps may appear similar to users, they differ significantly under the hood.
Installation, Accessibility, and User Reach
Mobile apps require users to download and install them, which creates a higher entry barrier but stronger retention once installed. Web apps are instantly accessible via URLs, making them easier to reach new users and share across platforms without friction.
Performance, Speed, and Offline Capabilities
Mobile apps generally offer superior performance because they run directly on the device and can store data locally. Web apps depend on browser performance and internet connectivity, although modern technologies have improved speed and caching.
User Experience and Interface Flexibility
Mobile apps offer richer user experiences by leveraging native UI components and gestures. Web apps prioritise consistency and responsiveness across devices, which may limit advanced interactions but improve accessibility.
Security, Updates, and Maintenance Requirements
Mobile apps require users to download updates, which can slow feature rollouts. Web apps update centrally, ensuring all users access the latest version instantly. Security management differs as mobile apps rely on app store guidelines, while web apps depend on server-side controls.
Cost, Development Time, and Long-Term Maintenance Comparison
Cost is often a deciding factor when choosing between a mobile app and a web app.
Initial Development Cost Considerations
Mobile apps typically require separate development for different platforms, increasing initial costs. Web apps usually involve a single codebase, making them faster and less expensive to develop initially.
Ongoing Maintenance and Update Costs
Maintaining multiple mobile platforms increases long-term costs. Web apps are easier to maintain since updates are applied once and reflected instantly across all users.
Scalability and Future Expansion Costs
Web apps scale more easily as user numbers grow, especially for global audiences. Mobile apps may require additional optimisation and infrastructure investment as usage increases.
Mobile App vs Web App: Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | Mobile App | Web App |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Required via app store | No installation required |
| Device Access | Full access to device hardware | Limited browser-based access |
| Performance | High and responsive | Dependent on browser & internet |
| Offline Support | Strong | Limited |
| Updates | User-dependent | Instant |
| Development Cost | Higher | Lower |
| SEO Visibility | Limited | Strong |
| User Engagement | Very high | Moderate |
Business Use Cases for Mobile Applications
Mobile apps are best suited for businesses that rely on frequent user interaction and personalised experiences.
When a Mobile App Is the Better Choice
If your business requires real-time notifications, offline access, or deep integration with device hardware, a mobile app is often the better solution. Apps are ideal when repeat usage is critical.
Industries That Benefit Most from Mobile Apps
Industries such as fintech, fitness, e-commerce, gaming, and on-demand services benefit greatly from mobile apps due to high engagement and performance requirements.
Customer Engagement and Retention Scenarios
Mobile apps enable push notifications, loyalty programs, and personalised content that strengthen long-term customer relationships.
Business Use Cases for Web Applications
Web apps excel in reach, accessibility, and content distribution.
When a Web App Makes More Sense
If your priority is fast deployment, wide accessibility, and frequent content updates, a web app is often the smarter choice.
Industries Suited for Web-Based Applications
Education platforms, SaaS tools, corporate portals, blogs, and marketplaces commonly rely on web apps for flexibility and SEO visibility.
SEO, Accessibility, and Content-Focused Use Cases
Web apps are discoverable through search engines, making them ideal for lead generation, informational platforms, and content-driven businesses.
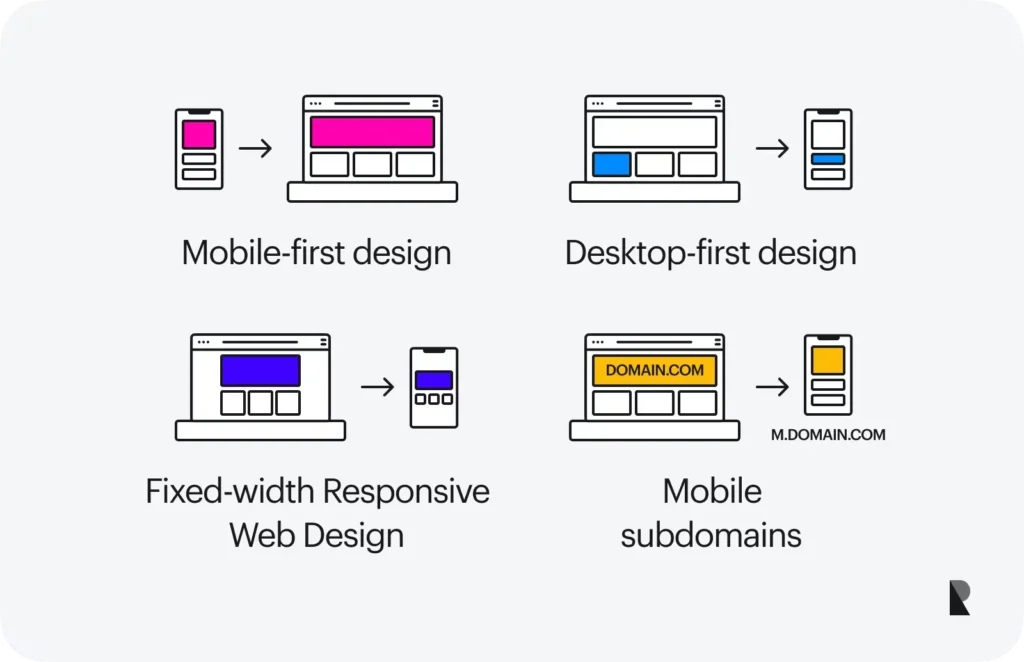
Progressive Web Apps (PWA): A Hybrid Alternative
PWAs combine the strengths of mobile apps and web apps into a single solution.
What Is a Progressive Web App?
A Progressive Web App is a web application that behaves like a mobile app. It can be installed on devices, work offline, and send notifications while remaining accessible via a browser. According to MDN Web Docs, Progressive Web Apps combine modern web capabilities with app-like experiences across devices.
Benefits of PWAs for Businesses
PWAs reduce development costs, improve performance, and enhance user experience without requiring full native app development.
When a PWA Can Replace a Mobile App
For businesses that want app-like features without app store dependency, PWAs can serve as a strong alternative.
How to Decide Between a Mobile App and a Web App
The right decision depends on strategic alignment, not trends. Broader insights on digital products, technology strategy, and modern business solutions are regularly shared on Influencers Gone Wild.
Defining Business Goals and Target Audience
Understanding who your users are and how they interact with your product is the first step. High engagement users may justify a mobile app, while broad audiences favour web apps.
Budget, Timeline, and Resource Availability
Limited budgets and tight timelines often favour web apps or PWAs, while long-term investments may justify mobile apps.
Required Features and Long-Term Strategy
Consider future needs such as scaling, integrations, and advanced features before committing to a platform.
Common Mistakes Businesses Make When Choosing an App Type
Many projects fail due to strategic misalignment rather than technical issues.
Overbuilding Without Validating User Needs
Building complex apps without understanding user demand often leads to low adoption.
Ignoring Maintenance and Update Costs
Long-term maintenance is frequently underestimated, especially for mobile apps.
Choosing Technology Over Business Goals
Technology should support business objectives, not dictate them.
Future Trends in App Development
App development continues to evolve with new technologies.
Cross-Platform and Hybrid App Development
Frameworks that support multiple platforms are reducing development time and cost.
AI and Automation in App Experiences
AI-driven personalisation, chatbots, and predictive features are becoming standard.
The Growing Role of PWAs and Cloud Apps
PWAs and cloud-native apps are gaining popularity due to flexibility and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Mobile Apps and Web Apps
Is a mobile app always better than a web app?
No, the best option depends on business goals, audience, and budget.
Can a web app later be converted into a mobile app?
Yes, many businesses start with web apps and expand to mobile later.
Are PWAs suitable for all businesses?
PWAs work best for content, e-commerce, and service platforms but may not replace all native apps.
Which option is better for SEO?
Web apps and PWAs offer significantly better SEO visibility than native mobile apps.
Final Thoughts on Choosing the Right App for Your Business
Choosing between a mobile app and a web app is a strategic business decision, not just a technical one. Mobile apps excel in performance and engagement, while web apps offer accessibility, scalability, and discoverability. Progressive Web Apps provide a compelling middle ground for many businesses.
The right choice depends on your audience, goals, budget, and long-term vision. By aligning technology with business strategy, you can build a digital solution that delivers lasting value and sustainable growth.






